Check your compliance!
helmut.minor • 11. Dezember 2023
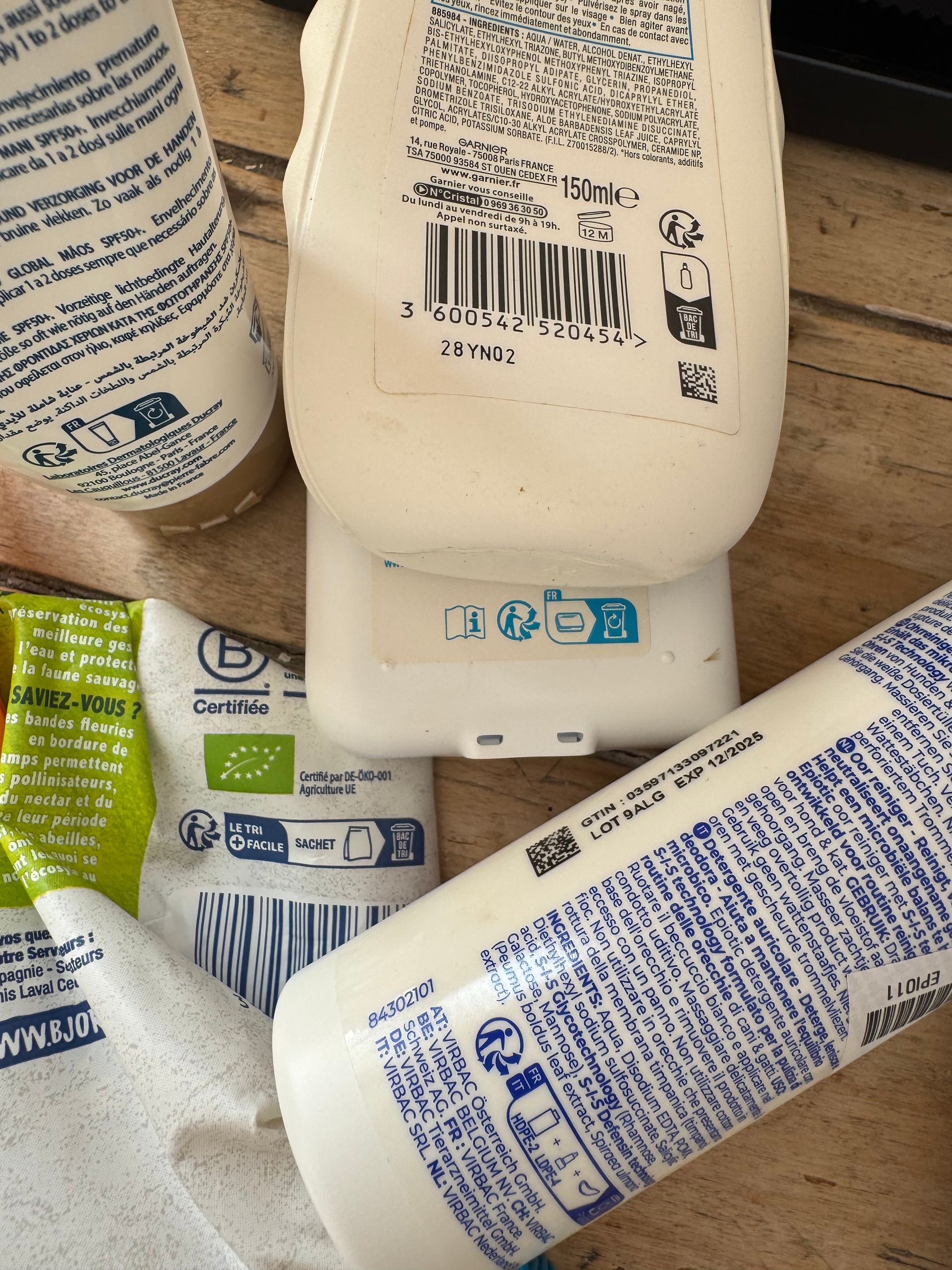
Registration for packaging EPR in Finland on the 1st January 2024.
Starting on the 1st January 2024, Finland no longer applies the threshold level of 1 Mio € revenue per year. Now every company that puts packaging onto the Finish market falls into the scope of the Finish packaging EPR.
Compliance is achieved through the participation in the collective scheme RINKI. The branding of RINKI can be applied onto the packaging, but there still is no mandatory labelling requirement in Finland.
Source: https://rinkiin.fi/en/news/

The Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) , part of the EU’s 2020 Circular Economy Action Plan and the European Green Deal, introduces the DPP to transform how products are tracked and managed across their lifecycle. Its core purpose is to support circular business models by providing accessible, reliable, and standardized data across the value chain. By digitizing lifecycle information, the DPP empowers recyclers with material-specific insights, enables manufacturers to monitor compliance, and helps consumers understand durability, repairability, and sustainability aspects. If implemented effectively, the DPP could become an important tool to drive real change in how products are produced, used, and recovered. But with the growing influence of Omnibus IV , a new question arises: Can the DPP remain a tool for circular innovation as it takes on a growing regulatory role under Omnibus IV? 1. Omnibus IV and the potential change of role of the DPP In a recent webinar, Arianee emphasized the alignment between the DPP and the Omnibus IV simplification initiative. A central proposal is to use the DPP to reduce reporting burdens for manufacturers by streamlining declarations of conformity, customs processes, and data exchange with authorities. The Omnibus IV package , published by the European Commission in May 2025, confirms this trajectory. From a regulatory standpoint, the DPP is becoming a powerful tool for administrative efficiency and digital integration across the Single Market. But this evolution also raises concerns. The DPP was designed to enable circular value creation , not just fulfill compliance obligations. If it becomes primarily a reporting mechanism for regulators, it could undermine its potential to support closed-loop systems, foster reuse, and unlock sustainability innovation. A balanced path is needed. One that aligns regulatory reliability with the practical needs of circular economy stakeholders. While regulatory alignment through Omnibus IV may provide much-needed structure , it risks narrowing the DPP’s functional scope . What qualifies as "compliance data" may fall short of what circular actors need, such as disassembly instructions, component-level material passports, or real-time usage data – and foremost inputs for a circular design of products. 2. Proof of concept: promising, but no common standard yet A pilot project launched in October 2024 by ecosystem , Fnac-Darty , Beko, Envie and Arianee marks one of the first large-scale implementations of the DPP for household appliances. Over two years, the initiative introduces digital passports built on Arianee’s open-source blockchain infrastructure , assigning each device a unique identity. These passports track lifecycle events, from manufacturing and market entry to repair, resale, and recycling. They also act as digital maintenance logs , consolidating technical specifications, repair history, and environmental impact into one accessible record. Crucially, the project is based on a non-proprietary, interoperable system , allowing data exchange between manufacturers, service providers, and recyclers. It demonstrates that the technology exists and that multi-stakeholder collaboration is possible. Yet a major obstacle remains: there is still no harmonized standard , neither sector-specific nor EU-wide. Without a shared framework, true interoperability remains out of reach. The ambition is clear, but the supporting infrastructure and governance lag behind. 3. Our impressions While the Digital Product Passport holds significant promise, our current impression is that its focus remains limited in several key areas, particularly when it comes to end-of-life processes and industrial usability. Strong emphasis on use phase: The DPP currently seems centered around extending product life, especially through improved repairability and maintenance transparency. However, its potential to support end-of-life processes seem less developed. Designed with the consumer in mind: Much of the DPP’s current design appears geared toward private end users, providing information that helps them repair or understand the sustainability of a product. In contrast, there seems to not be too much focus on industrial users. Questions around data quality and control: Another open issue is the quality of the data entered into the DPP. Since its usefulness depends on accurate and comprehensive input, the question arises: Who validates this information, and how is data quality ensured across different actors and sectors? At this stage, we see a lack of clear governance mechanisms for data verification. A tool for customer engagement, but what about EoL? From the manufacturer's perspective, the DPP seems to offer value primarily as a customer retention tool, for example, through transparent communication about product features and sustainability. However, it remains unclear what incentive manufacturers have to provide detailed and useful end-of-life data, especially if it does not serve their immediate business interests. Looking ahead, several important questions remain unanswered: Can the DPP be scaled to support end-of-life processes at an industrial level? Is it possible for recyclers to extract and interpret high-volume data to improve recycling workflows? Could the DPP support the development of a functioning secondary market for spare parts and recovered materials that is economically viable? In our view, there may currently be more expected of the DPP’s role in end-of-life than it is yet able to deliver. Much will depend on how the system evolves in the coming years—both technically and in terms of regulatory and industry adoption. 4. So, catalyst or casualty? At this stage, the DPP is both : For one it is a catalyst in its intention, design, and pilot implementations . On the other, it is a potential casualty in its institutional framing under Omnibus IV . Whether it fulfills its promise will depend on political will, cross-sector collaboration, and a conscious effort to anchor the DPP in real-world circular value, not just administrative logic. To succeed, the DPP must do more than simplify processes. It must enable circular outcomes. Only if the DPP offers tangible value to both regulators and market actors can it truly fulfill its intended role as a driver of sustainability in Europe’s product economy. And that means putting data, users, and material recovery - not just regulatory compliance - at the center of its evolution.